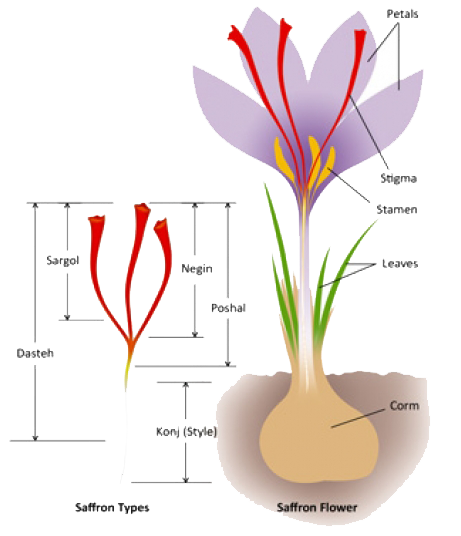
Saffron is one of the highly prized spices known since antiquity for its color, flavor and medicinal properties and also can be used as a fabric dye. It is the dried "stigma" or threads of the flower of the Crocus sativus plant. It is a bulbous perennial plant that belongs to the family of Iridaceae, in the genus, Crocus, and known botanically as Crocus sativus.
The Crocus sativus plant grows to about 15-20cm in height and bears lavender colored flowers during each season which lasts from October until November. Each flower features perianth consisting of a stalk, known as “style,” connecting to three “stigmas” or threads to the rest of the plant. These red-yellow colored stigmas along with the "style" constitutes "saffron" which is used as condiment spice. Saffron has been the world’s most expensive spice by weight for decades. It takes 150,000 flowers to make 1 kilogram of saffron.
Good saffron crop production demands cool dry climate with well-drained rich fertile soil and irrigation facilities or sufficient amount of rain fall. The flowers are generally harvested during the early-morning hours and soon their stigma separated, allowed to dry, and packed for marketing.
Saffron has a distinct flavor that comes from chemical compounds in it such as picrocrocin, and safranal. It also contains a natural carotenoid chemical compound, crocin, which gives saffron its golden-yellow hue. These traits along with its medicinal properties make it a valuable ingredient in many cuisines worldwide.